|
|
|
An asymptotic series is a Series Expansion of a Function in a variable ![]() which may converge or diverge (Erdelyi
1987, p. 1), but whose partial sums can be made an arbitrarily good approximation to a given function for large enough
which may converge or diverge (Erdelyi
1987, p. 1), but whose partial sums can be made an arbitrarily good approximation to a given function for large enough ![]() . To
form an asymptotic series
. To
form an asymptotic series ![]() of
of
![]() , written
, written
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
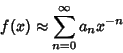 |
(6) |
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.).
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, p. 15, 1972.
Arfken, G. ``Asymptotic of Semiconvergent Series.'' §5.10 in
Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 339-346, 1985.
Bleistein, N. and Handelsman, R. A. Asymptotic Expansions of Integrals. New York: Dover, 1986.
Copson, E. T. Asymptotic Expansions. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1965.
de Bruijn, N. G. Asymptotic Methods in Analysis, 2nd ed. New York: Dover, 1982.
Dingle, R. B. Asymptotic Expansions: Their Derivation and Interpretation. London: Academic Press, 1973.
Erdelyi, A. Asymptotic Expansions. New York: Dover, 1987.
Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. ``Asymptotic Series; Method of Steepest Descent.'' §4.6 in
Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 434-443, 1953.
Olver, F. W. J. Asymptotics and Special Functions. New York: Academic Press, 1974.
Wasow, W. R. Asymptotic Expansions for Ordinary Differential Equations. New York: Dover, 1987.
![]() Asymptotic Series
Asymptotic Series
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein