Defined by
![\begin{displaymath}[l]\equiv {1-q^l\over 1-q}
\end{displaymath}](g_967.gif) |
(1) |
for integral 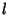 , and
, and
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[{\matrix{n\cr k\cr}}\right]\equiv\cases{
\prod_{l=1}^k {[n-l+1]\over [l]} & for $0\leq k\leq n$\cr
0 & otherwise.\cr}
\end{displaymath}](g_969.gif) |
(2) |
Unfortunately, the Notation conflicts with that of Gaussian Brackets and the Nearest Integer Function. Gaussian
Polynomials satisfy the identities
![\begin{displaymath}
{\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k+1\cr}}\right]\over\left[{\matrix{n\cr k+1\cr}}\right]}={1-q^{n+1}\over 1-q^{n-k}}
\end{displaymath}](g_970.gif) |
(3) |
![\begin{displaymath}
{\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k+1\cr}}\right]\over\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k\cr}}\right]}={1-q^{n-k+1}\over 1-q^{k+1}}.
\end{displaymath}](g_971.gif) |
(4) |
For 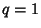 , the Gaussian polynomial turns into the Binomial Coefficient.
, the Gaussian polynomial turns into the Binomial Coefficient.
See also Binomial Coefficient, Gaussian Coefficient, q-Series
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-25
![\begin{displaymath}
{\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k+1\cr}}\right]\over\left[{\matrix{n\cr k+1\cr}}\right]}={1-q^{n+1}\over 1-q^{n-k}}
\end{displaymath}](g_970.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
{\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k+1\cr}}\right]\over\left[{\matrix{n+1\cr k\cr}}\right]}={1-q^{n-k+1}\over 1-q^{k+1}}.
\end{displaymath}](g_971.gif)